How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding the various types and their unique flight characteristics to mastering advanced maneuvers and adhering to safety regulations. We’ll explore pre-flight checks, basic and advanced controls, and even delve into the art of aerial photography and videography.
Prepare to take flight into the world of drone piloting!
Whether you’re a complete beginner or have some prior experience, this comprehensive guide provides a structured approach to learning, covering everything from selecting the right drone to troubleshooting common issues. We’ll break down complex concepts into easily digestible steps, ensuring you gain the confidence and knowledge to operate your drone safely and responsibly.
Drone Types and Their Operation
Understanding the different types of drones and their operational characteristics is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will explore the key differences between various drone designs, their control interfaces, and their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Quadcopter, Hexacopter, and Octocopter Operation
These multirotor drones differ primarily in the number of rotors. Quadcopters, with four rotors, are the most common, offering a good balance of stability and maneuverability. Hexacopters (six rotors) and octocopters (eight rotors) provide increased redundancy and stability, making them suitable for heavier payloads or more challenging flight conditions. A failed rotor on a quadcopter will likely result in a crash, whereas a hexacopter or octocopter can often maintain flight even with one or two rotor failures.
Operationally, the control principles remain largely the same across these types, although the increased stability of hexa- and octocopters may require slightly different piloting techniques for precise maneuvers.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the basics is crucial before taking to the skies, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from safety protocols to advanced maneuvers. Ultimately, safe and effective drone piloting requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology.
Fixed-Wing and Multirotor Flight Characteristics
Fixed-wing drones, resembling miniature airplanes, rely on forward momentum for lift, offering longer flight times and greater range compared to multirotor drones. However, they require a runway for takeoff and landing and are less maneuverable, especially at low speeds. Multirotor drones, on the other hand, can take off and land vertically, making them ideal for confined spaces and precise hovering.
Their superior maneuverability allows for intricate aerial photography and videography. The control interfaces and piloting techniques are significantly different between these two types.
Drone Control Interfaces
Drone control interfaces vary widely. Many drones utilize dedicated joysticks offering precise control over throttle, pitch, roll, and yaw. Others offer app-based control via smartphones or tablets, providing a more intuitive and accessible interface, although potentially less precise than a joystick. Some high-end drones integrate both joystick and app control for versatility. The choice of control interface depends on personal preference, drone capabilities, and the complexity of the intended operation.
Comparison of Drone Propulsion Systems, How to operate a drone
The choice of propulsion system significantly impacts drone performance and characteristics. Below is a comparison of common systems:
| Propulsion System | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brushless Motors | High efficiency, long lifespan, powerful | Higher initial cost | Most drones, especially larger/heavier models |
| Brushed Motors | Lower initial cost | Lower efficiency, shorter lifespan, less powerful | Smaller, less demanding drones |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight check is paramount for safe and legal drone operation. Neglecting this crucial step can lead to accidents and legal repercussions. This section Artikels the essential steps involved in a comprehensive pre-flight inspection.
Pre-Flight Inspection Steps
Before each flight, a comprehensive pre-flight inspection should be conducted. This involves visually inspecting the drone for any damage to propellers, arms, or other components. Check all connections to ensure they are secure. Furthermore, confirming the proper functionality of all components, such as the camera and GPS, is crucial.
Importance of Battery, Signal, and GPS Checks
Battery levels should always be checked before each flight to avoid mid-flight power failures. Signal strength should be assessed to ensure reliable communication between the drone and the controller. GPS connectivity is vital for accurate positioning and autonomous flight modes; ensure a strong GPS signal before takeoff.
Drone Safety and Legal Operation Checklist
- Inspect drone for physical damage
- Check battery level and charge
- Verify GPS signal strength
- Confirm controller connection
- Check local airspace restrictions
- Ensure compliance with all relevant regulations
- Inform relevant parties about your flight plan (if necessary)
Pre-Flight Sequence Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight sequence would enhance understanding. Imagine a flowchart starting with “Power on Controller,” followed by “Check Battery,” “Check GPS,” “Check Propellers,” and culminating in “Initiate Takeoff.” Each step would be visually linked, creating a clear path.
Basic Drone Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the basic controls and maneuvers is essential for safe and effective drone operation. This section will cover the fundamental controls, takeoff and landing procedures, and basic flight movements.
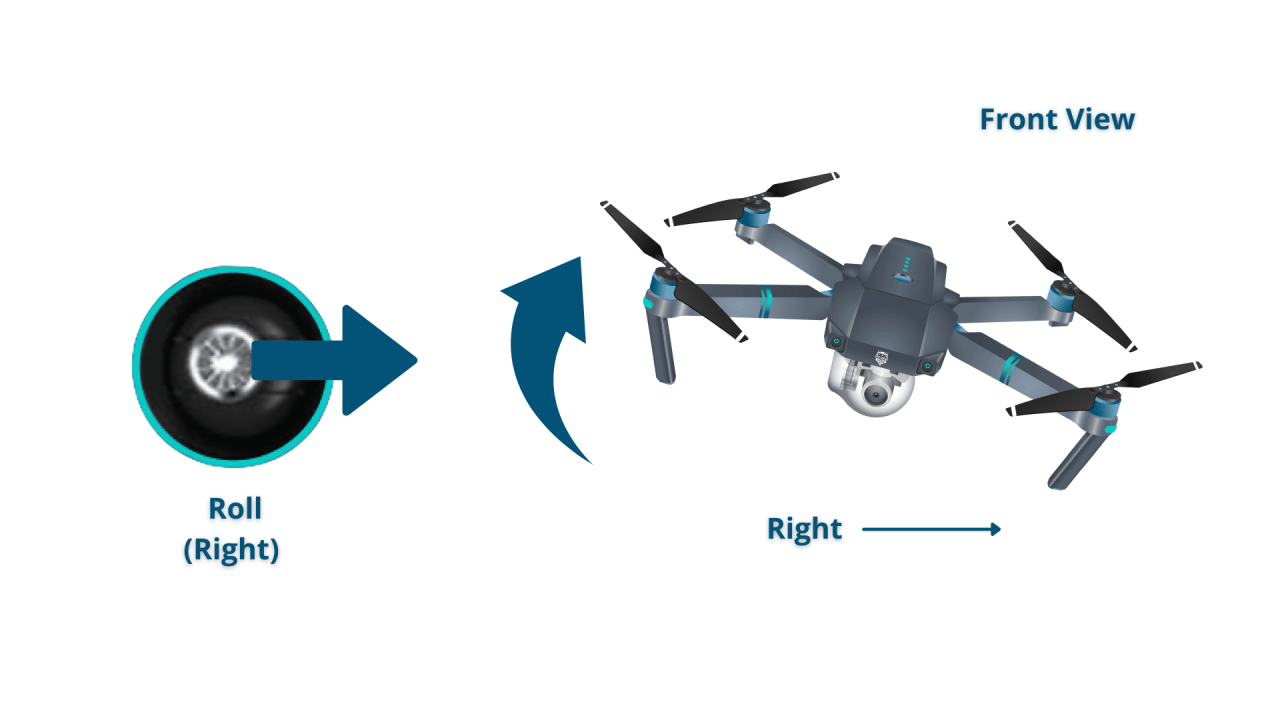
Throttle, Pitch, Roll, and Yaw Controls
The throttle controls the drone’s altitude, increasing or decreasing its vertical speed. Pitch controls the forward and backward movement, while roll controls the sideways movement (left and right). Yaw controls the drone’s rotation around its vertical axis (turning left or right).
Takeoff, Landing, and Hovering Techniques
Takeoff typically involves gently increasing the throttle until the drone lifts off the ground. Maintaining a steady throttle allows for hovering. Landing involves gradually decreasing the throttle until the drone gently touches down. Smooth, controlled movements are key to safe takeoff and landing.
Basic Maneuvers: Forward, Backward, Sideways, and Diagonal
Basic maneuvers are achieved by combining pitch and roll controls. Moving forward involves gently pushing the pitch stick forward, backward movement involves pulling it back. Sideways movement utilizes the roll stick, and diagonal movement combines pitch and roll.
Common Beginner Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Sudden movements: Avoid jerky movements; use smooth, controlled inputs.
- Ignoring battery level: Always monitor battery level and land before it gets too low.
- Losing sight of the drone: Maintain visual contact with the drone at all times.
- Flying in prohibited airspace: Check airspace restrictions before flying.
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques: How To Operate A Drone
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore more advanced flight techniques to enhance your drone piloting skills. These techniques require practice and a good understanding of drone dynamics.
Complex Maneuvers: Flips, Rolls, and Spins
Flips, rolls, and spins are acrobatic maneuvers requiring precise and coordinated control inputs. These are typically enabled through specific modes within the drone’s control software. Mastering these maneuvers requires significant practice and understanding of the drone’s capabilities and limitations.
Waypoint Navigation and Autonomous Flight Modes
Many drones offer waypoint navigation, allowing you to program a flight path by setting a series of waypoints. Autonomous flight modes automate certain flight functions, such as returning to home or following a pre-programmed path. These features can significantly simplify complex flights.
Achieving Smooth and Precise Drone Control

Smooth and precise control comes with practice. Start with slow, deliberate movements, gradually increasing speed and complexity as your skills improve. Using smaller, more controlled stick inputs will help you achieve greater precision.
Flying in Challenging Conditions (Wind, Rain)
- Wind: Fly in calmer conditions whenever possible. If wind is present, adjust your piloting technique to compensate for wind drift.
- Rain: Avoid flying in rain as it can damage the drone’s electronics and reduce visibility.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning photos and videos. This section will explore techniques for optimizing image and video quality and creating compelling aerial content.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Quality
Understanding your drone’s camera settings is essential for capturing high-quality images and videos. Adjusting settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture allows you to control exposure, depth of field, and motion blur.
Capturing Different Types of Shots (Aerial Panoramas, Cinematic Footage)
Aerial panoramas are created by stitching together multiple overlapping photos. Cinematic footage involves using smooth, deliberate movements to create visually engaging videos. Experiment with different camera angles and perspectives to achieve the desired aesthetic.
Using Drone-Specific Features (Gimbal Control, Focus Adjustments)
Many drones feature gimbals that stabilize the camera, allowing for smoother shots, especially in windy conditions. Understanding and utilizing gimbal control and focus adjustments will greatly enhance the quality of your aerial photography and videography.
Composing Effective Aerial Shots (Rule of Thirds, Leading Lines)
Applying composition techniques like the rule of thirds and leading lines will improve the visual appeal of your aerial shots. The rule of thirds suggests placing key elements off-center for a more balanced and visually interesting composition. Leading lines draw the viewer’s eye through the image, creating depth and visual interest.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Adhering to local drone regulations and safety practices is crucial for responsible drone operation. This section will Artikel the importance of compliance and safe operating procedures.
Adhering to Local Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Before flying, always check local regulations and airspace restrictions. Many countries and regions have specific rules regarding where and when you can fly a drone. Failing to comply can result in fines or legal action.
Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Drone operation carries inherent risks, including collisions, loss of control, and damage to property. Mitigation strategies include regular pre-flight checks, maintaining visual contact with the drone, and flying in appropriate conditions.
Best Practices for Responsible Drone Operation
- Maintain a safe distance from people and property.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Respect the privacy of others.
- Fly responsibly and avoid reckless behavior.
Airspace Classifications and Implications
A table illustrating typical airspace classifications and their implications for drone pilots would be beneficial. This table could include categories like Class G (uncontrolled), Class E (controlled), and Class B (major airports), along with the respective restrictions and requirements for drone operation in each class.
| Airspace Class | Description | Drone Operation Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
| Class G | Uncontrolled airspace | Generally less restrictive, but still subject to other regulations |
| Class E | Controlled airspace | May require authorization or specific flight plans |
| Class B | Major airport airspace | Strict restrictions, usually requiring prior authorization |
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Understanding common drone malfunctions and how to troubleshoot them is essential for maintaining a functional drone and ensuring safe operation. This section will provide guidance on identifying and resolving common issues.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common malfunctions include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor failure, and communication issues. These issues can stem from various causes, including depleted batteries, interference, physical damage, or software glitches.
Troubleshooting Guides for Resolving Issues
Troubleshooting involves systematically checking different components and settings. For example, if the drone loses GPS signal, check for obstructions and ensure the GPS module is functioning correctly. If a motor fails, visually inspect it for damage and replace it if necessary.
Importance of Regular Drone Maintenance
Regular maintenance, including cleaning propellers, checking for loose parts, and calibrating sensors, helps prevent malfunctions and extends the lifespan of your drone.
Resources for Technical Support and Repairs

Manufacturers typically provide support documentation and contact information. Online forums and communities dedicated to drone operation can be valuable resources for troubleshooting and finding repair services.
Mastering drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and practice. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of the essential skills and knowledge required for safe and responsible drone piloting. Remember to always prioritize safety, adhere to local regulations, and continuously refine your skills through practice and further exploration. The skies await – fly responsibly and enjoy the incredible perspectives that drone technology offers!
FAQs
What is the best drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones are available for beginners. Look for features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home functionality, and easy-to-use controls via an app.
How long does a drone battery last?
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires careful attention to detail, and a good starting point is learning the basics; you can find comprehensive guidance on this at how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology.
Drone battery life varies depending on the model and usage. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge. Always carry extra batteries.
What happens if I lose the drone’s signal?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) feature that automatically guides the drone back to its starting point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight.
Do I need a license to fly a drone?
Regulations vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority to determine any licensing or registration requirements before flying.
